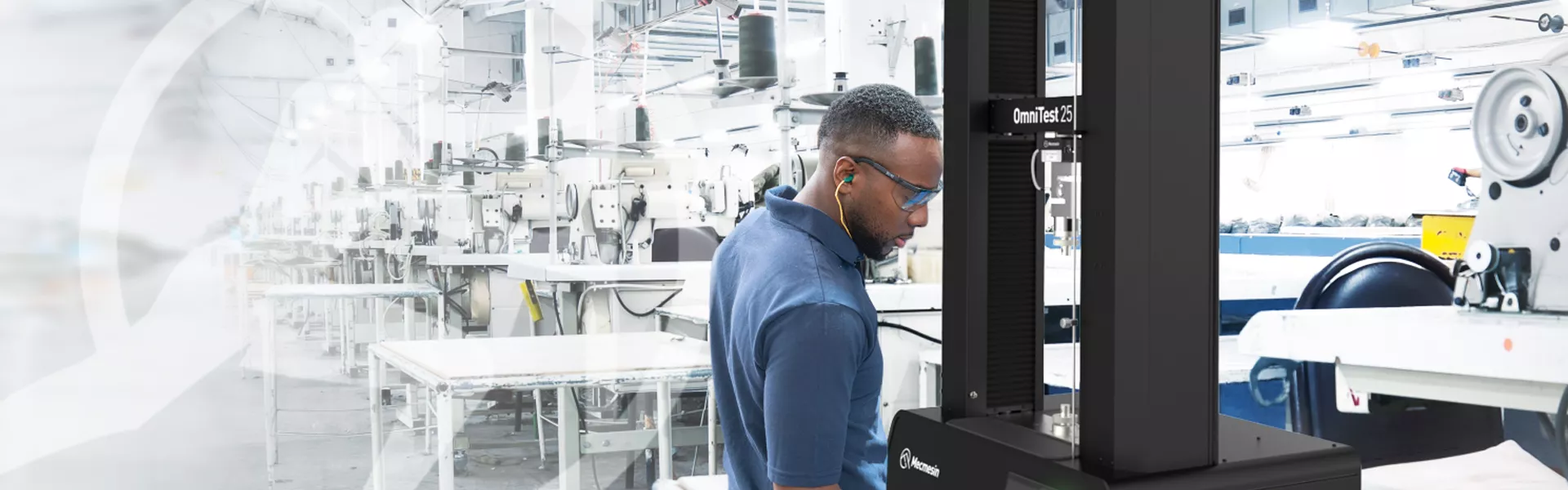

We help you select the best solution to meet your needs
As simple as that may sound, there are many different options available when it comes to choosing a tensile tester. All of our tensile testers can also be used for compression testing.
Ensuring product safety and performance through Tensile testing
Tensile testing has long been an important part of design and quality control for ensuring product safety and performance. It is also an essential part of the testing regime which helps deliver cost-effective consistency and efficiency in manufacturing and assembly. By following these nine steps, you can select the most appropriate tensile tester for your testing requirements.
Test requirements
Answer
Define your testing requirements
- Identify the materials or products you will be testing
- Determine the testing application(s) and any specific data you need to collect



Tensile testers can be implemented in many areas including research and development, quality control, goods-in inspection and production.
Before you begin looking for a tensile tester, you need to define your testing requirements. This includes identifying the materials or products you will be testing and determining the testing application and test methods you wish to follow. Don’t forget that all tensile testers can also be configured to perform testing in compression. For this reason, they are also commonly known as UTMs ‘Universal Testing Machines’.
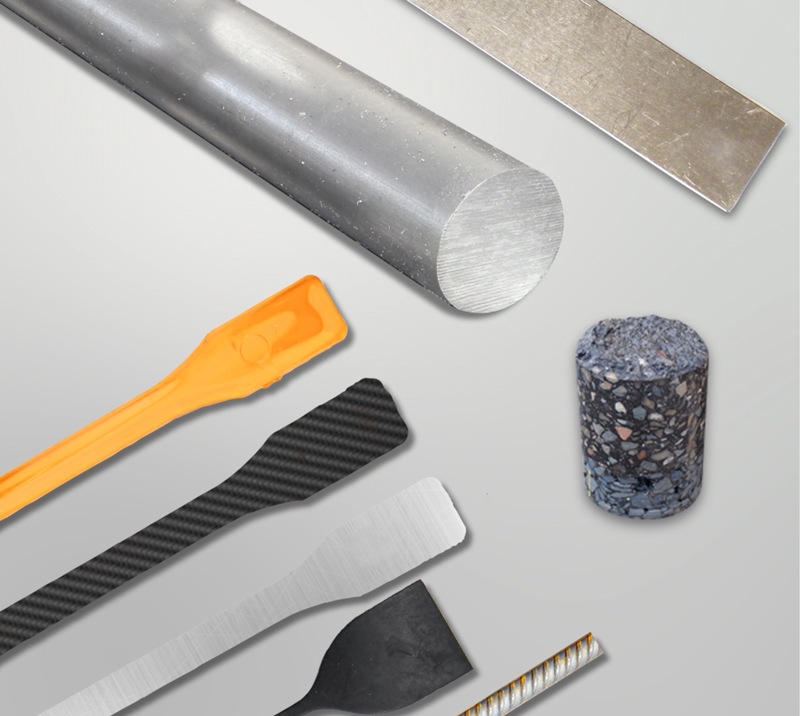 Materials and Products
Materials and Products
The first step in defining your testing requirements is to identify the materials or products you will be testing. Tensile testers can be used to test a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, rubber, textiles, paper and much more.
By identifying which materials or products you will be testing, you can then investigate which physical properties are the most important for you to measure and record. Tensile strength, compressive resistance, peel and frictional strength are just some of the many properties that can be measured using a tensile tester.
Testing Application and Data Collection
Once you have determined the testing application, you can then investigate whether there are any industry or international standards that describe an appropriate test method to follow. You may decide that you prefer to follow specific standards or adapt the testing methods to suit your own requirements.
Each application may require several types of data collection, such as stress-strain curves, yield strength, or ultimate tensile strength. By identifying the specific data you need to collect, you can ensure that the tensile tester is equipped to provide it.
Once you have defined your immediate testing requirements, you can then consider whether you are likely to have any additional requirements in the future and what they might be. By taking the time to define your testing requirements upfront, you can ensure that you are in the best position to choose a tensile tester that is suitable for all your specific needs.
Define your testing requirements
- Identify the materials or products you will be testing
- Determine the testing application(s) and any specific data you need to collect



Tensile testers can be implemented in many areas including research and development, quality control, goods-in inspection and production.
Before you begin looking for a tensile tester, you need to define your testing requirements. This includes identifying the materials or products you will be testing and determining the testing application and test methods you wish to follow. Don’t forget that all tensile testers can also be configured to perform testing in compression. For this reason, they are also commonly known as UTMs ‘Universal Testing Machines’.

The first step in defining your testing requirements is to identify the materials or products you will be testing. Tensile testers can be used to test a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, rubber, textiles, paper and much more.
By identifying which materials or products you will be testing, you can then investigate which physical properties are the most important for you to measure and record. Tensile strength, compressive resistance, peel and frictional strength are just some of the many properties that can be measured using a tensile tester.
Testing Application and Data CollectionOnce you have determined the testing application, you can then investigate whether there are any industry or international standards that describe an appropriate test method to follow. You may decide that you prefer to follow specific standards or adapt the testing methods to suit your own requirements.
Each application may require several types of data collection, such as stress-strain curves, yield strength, or ultimate tensile strength. By identifying the specific data you need to collect, you can ensure that the tensile tester is equipped to provide it.
Once you have defined your immediate testing requirements, you can then consider whether you are likely to have any additional requirements in the future and what they might be. By taking the time to define your testing requirements upfront, you can ensure that you are in the best position to choose a tensile tester that is suitable for all your specific needs.


Load capacity
Answer
Choose the suitable Load capacity
- Identify the maximum load needed for your testing requirements
- Ensure that the tensile tester can accommodate your maximum load capacity
- Ensure that loadcells are available to meet the min and max load requirements
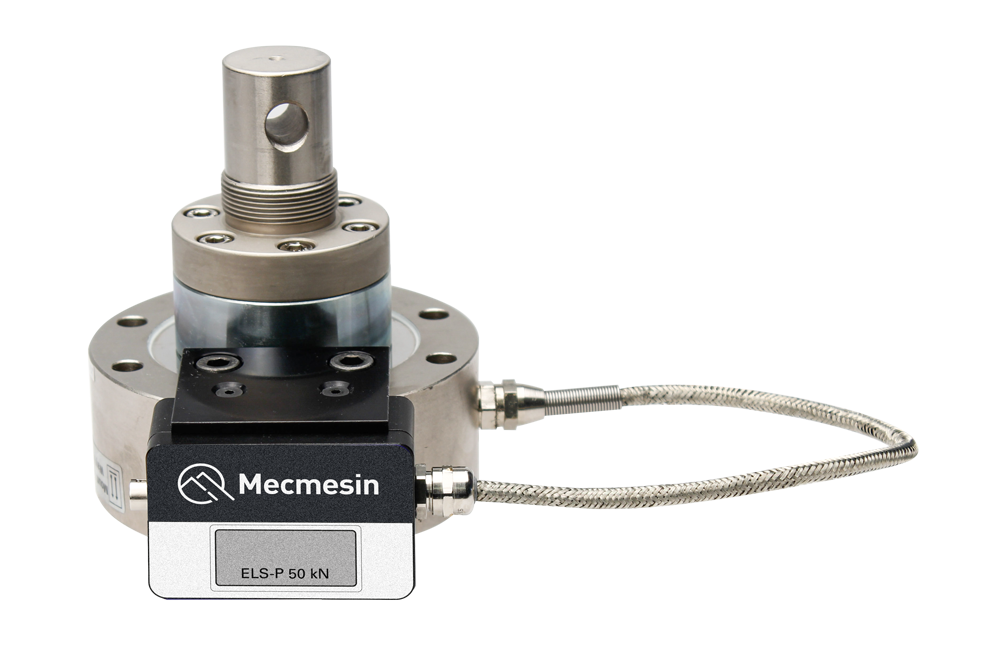




After defining your testing requirements, the next step is to choose the right load capacity for your tensile tester. Load capacity refers to the maximum force or weight that a tensile tester can apply to a specimen during testing. It is usually expressed in kN (kilonewtons) or lbf (pounds-force). Each tensile tester has a maximum rated capacity that must not be exceeded when testing.
Identifying Your Load Capacity Needs
To choose the right load capacity of your tensile tester, you need to identify the maximum load needed to test your specimens. This will depend on the type of materials or products you are testing and the specific testing requirements. For example, testing a metal beam may require a much higher load capacity than testing a piece of fabric. Your test methods may require non-destructive testing (apply a certain load and stop) or destructive testing (apply a load until the specimen breaks). It is always a good idea to allow an extra safety margin of at least 10% above the maximum load you wish to apply when selecting a tensile tester.
Ensure Compatibility with Your Maximum Load Capacity Needs
Once you have identified your load capacity needs, it is important to ensure that the tensile tester you choose can accommodate those needs. Tensile testers are typically available in a range of load capacities, from small table-top models that can test loads of a few kilonewtons to large floor-standing models that can test loads of hundreds of kilonewtons. Choosing the right load capacity is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable testing results. Choosing a tensile tester with a load capacity that is too low for your testing requirements will mean that you cannot complete all tests. Choosing a tensile tester with a load capacity that is too high can be unnecessarily expensive and require excessive after-sales costs.
Ensure you can test across the full range of your Load requirements
Once you have identified your maximum load capacity, you should consider the minimum loads at which you will be testing. This is important because it will help you decide whether you will need to buy several loadcells to cover your complete range of testing.
Each loadcell has an accuracy specification and it is good practice to select a loadcell which has sufficient precision to allow you to test with confidence and repeatability. Testing a thin metal wire to a few newtons with a loadcell rated to several kilonewtons (that you might use for testing a large metal rod) will mean that the results obtained may not have the precision you require.
The good news is that most tensile testers offer a wide selection of loadcells to cover the range of testing and they are usually quick and easy to interchange.
Choose the suitable Load capacity
- Identify the maximum load needed for your testing requirements
- Ensure that the tensile tester can accommodate your maximum load capacity
- Ensure that loadcells are available to meet the min and max load requirements




After defining your testing requirements, the next step is to choose the right load capacity for your tensile tester. Load capacity refers to the maximum force or weight that a tensile tester can apply to a specimen during testing. It is usually expressed in kN (kilonewtons) or lbf (pounds-force). Each tensile tester has a maximum rated capacity that must not be exceeded when testing.
Identifying Your Load Capacity NeedsTo choose the right load capacity of your tensile tester, you need to identify the maximum load needed to test your specimens. This will depend on the type of materials or products you are testing and the specific testing requirements. For example, testing a metal beam may require a much higher load capacity than testing a piece of fabric. Your test methods may require non-destructive testing (apply a certain load and stop) or destructive testing (apply a load until the specimen breaks). It is always a good idea to allow an extra safety margin of at least 10% above the maximum load you wish to apply when selecting a tensile tester.
Ensure Compatibility with Your Maximum Load Capacity NeedsOnce you have identified your load capacity needs, it is important to ensure that the tensile tester you choose can accommodate those needs. Tensile testers are typically available in a range of load capacities, from small table-top models that can test loads of a few kilonewtons to large floor-standing models that can test loads of hundreds of kilonewtons. Choosing the right load capacity is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable testing results. Choosing a tensile tester with a load capacity that is too low for your testing requirements will mean that you cannot complete all tests. Choosing a tensile tester with a load capacity that is too high can be unnecessarily expensive and require excessive after-sales costs.
Ensure you can test across the full range of your Load requirementsOnce you have identified your maximum load capacity, you should consider the minimum loads at which you will be testing. This is important because it will help you decide whether you will need to buy several loadcells to cover your complete range of testing.
Each loadcell has an accuracy specification and it is good practice to select a loadcell which has sufficient precision to allow you to test with confidence and repeatability. Testing a thin metal wire to a few newtons with a loadcell rated to several kilonewtons (that you might use for testing a large metal rod) will mean that the results obtained may not have the precision you require.
The good news is that most tensile testers offer a wide selection of loadcells to cover the range of testing and they are usually quick and easy to interchange.
Grips/fixtures
Answer
Check grip and fixture requirements
- Determine whether standard grips and fixtures are suitable for holding your materials or products
- Consider custom grip and fixture design if needed
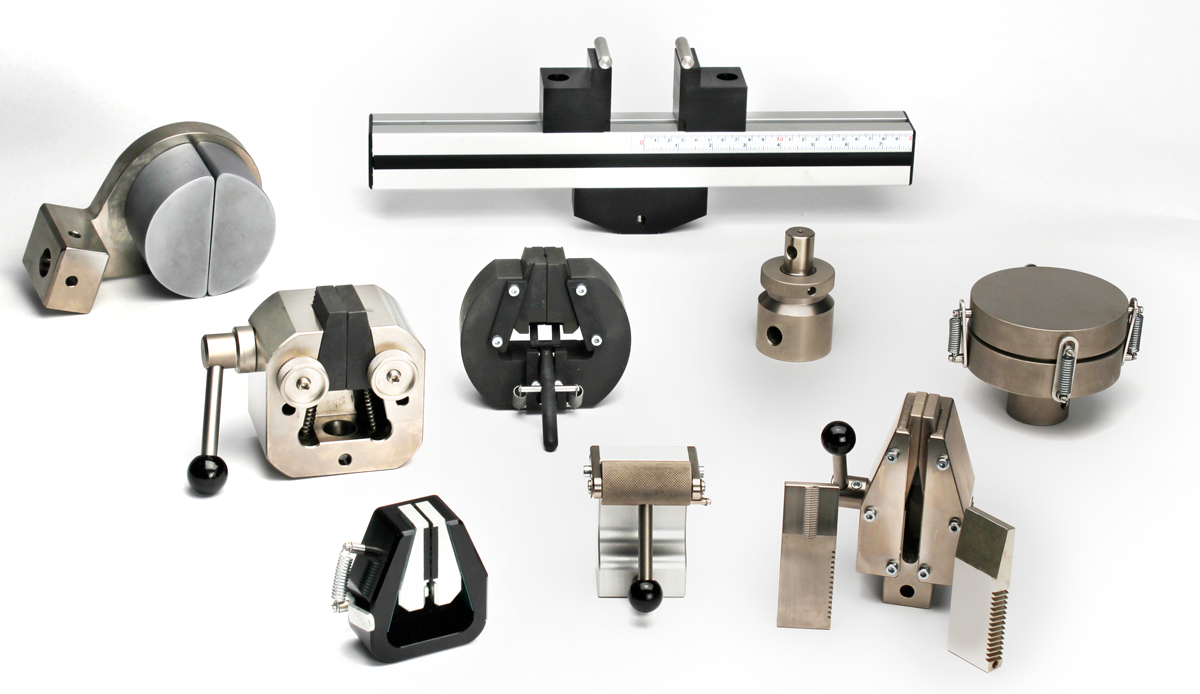
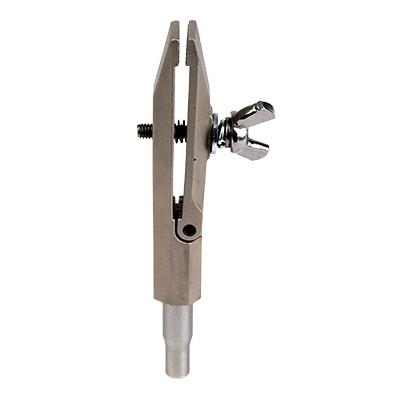



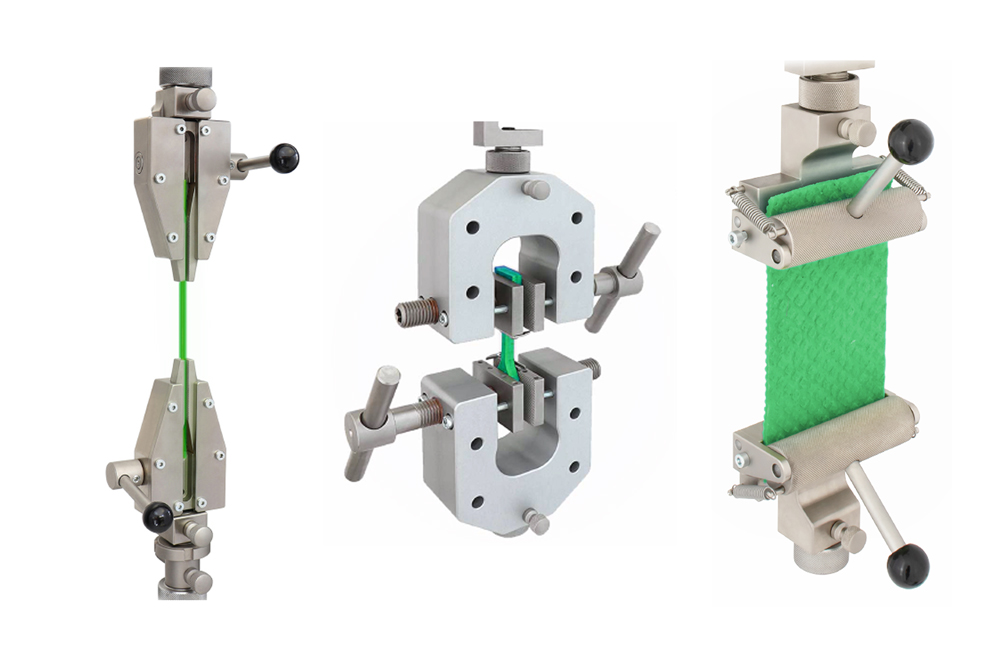
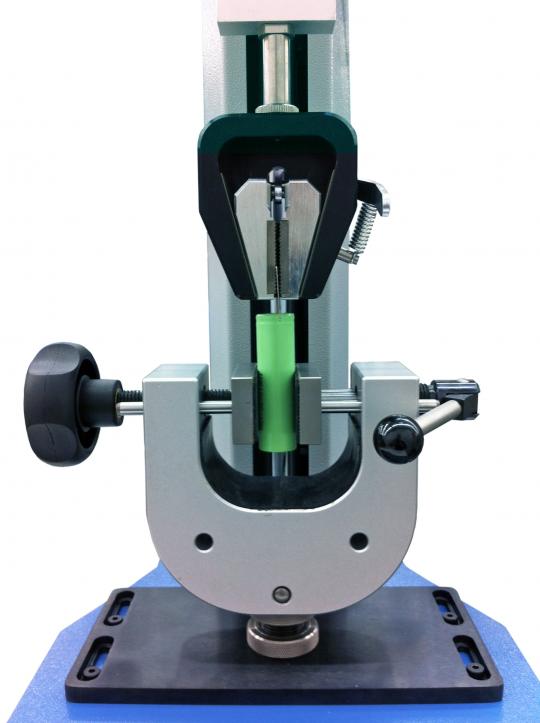
Based on the maximum and minimum load requirements you have established it is now time to select the grips and fixtures to hold your materials and products during testing. This is sometimes the trickiest part of choosing a tensile tester.
If you have a range of materials or products to test it may not be possible to use a single universal grip to hold all specimens. You will probably need to choose several grips and maybe also a selection of jaw faces suited to your specimens. Selecting jaw faces is always a trade-off between using a jaw profile that is sufficient to hold the specimen without slipping but is not too ‘aggressive’ to bite into the material to cause damage.
Grips can be manually operated (where the user tightens and releases the jaws) or they can be pneumatically operated (where the user presses a lever or footswitch to tighten and release the jaws). A compressed air supply is required for pneumatic grips.
Each grip will have a general maximum load rating that should not be exceeded.
If standard grips and fixtures are not suitable for holding your materials or products, it may be necessary to use custom-built grips. A good supplier of tensile testers can help and advise on suitable grips based on their experience.
Note the dimensions of the largest grip you will use since this will be a factor in the next step of choosing your tensile tester.
Check grip and fixture requirements
- Determine whether standard grips and fixtures are suitable for holding your materials or products
- Consider custom grip and fixture design if needed




Based on the maximum and minimum load requirements you have established it is now time to select the grips and fixtures to hold your materials and products during testing. This is sometimes the trickiest part of choosing a tensile tester.
If you have a range of materials or products to test it may not be possible to use a single universal grip to hold all specimens. You will probably need to choose several grips and maybe also a selection of jaw faces suited to your specimens. Selecting jaw faces is always a trade-off between using a jaw profile that is sufficient to hold the specimen without slipping but is not too ‘aggressive’ to bite into the material to cause damage.
Grips can be manually operated (where the user tightens and releases the jaws) or they can be pneumatically operated (where the user presses a lever or footswitch to tighten and release the jaws). A compressed air supply is required for pneumatic grips.
Each grip will have a general maximum load rating that should not be exceeded.
If standard grips and fixtures are not suitable for holding your materials or products, it may be necessary to use custom-built grips. A good supplier of tensile testers can help and advise on suitable grips based on their experience.
Note the dimensions of the largest grip you will use since this will be a factor in the next step of choosing your tensile tester.
Workspace
Answer
Choose the suitable travel stroke and workspace
- Identify the maximum travel distance required when the material or product is being stretched. Ensure that the tensile tester can accommodate your maximum stretch distance (known as “crosshead travel”).
- Check that the material or product you are testing can fit comfortably onto the workspace area of the tensile tester (known as ‘throat depth’).
- If ‘crosshead travel’ or ‘throat depth’ is insufficient you may need to consider a larger tensile tester even if it is nominally rated to a much higher load capacity than you need.



Having defined your test requirements and selected the load range you need, it is now time to consider the dimensional aspects of your testing.
Calculating Travel Distance

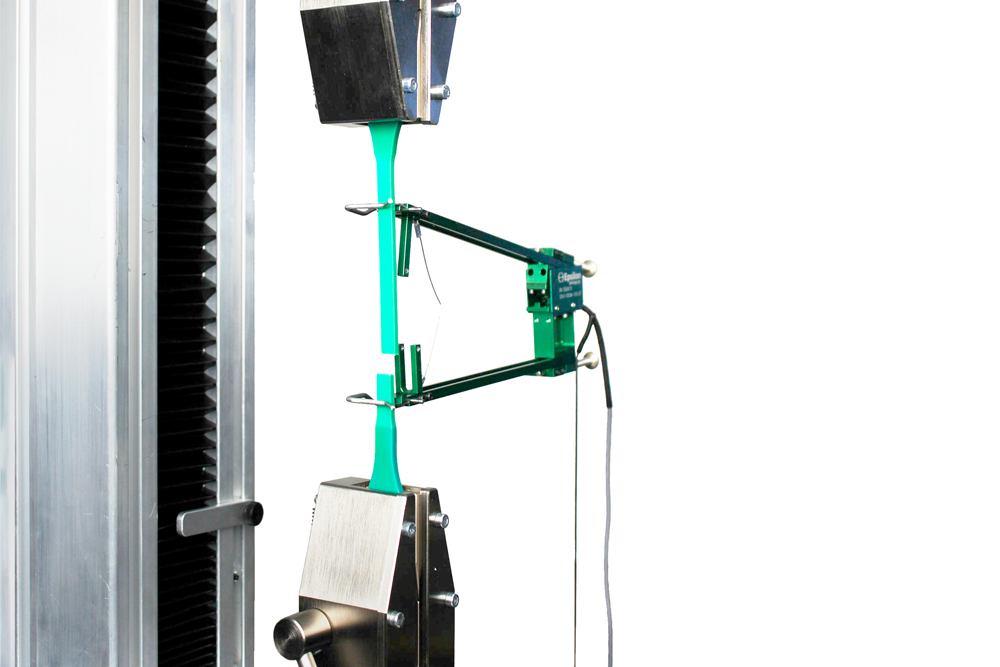
If you are performing tensile test you will need to identify the maximum travel distance required when the material or product is being stretched. Start with defining your initial specimen length and estimate the elongation that you expect to see. This will allow you to calculate the ‘crosshead travel’ that you require. Do not forget to include in your calculations the height of the grips you will use to hold the material/product, as these take up room on the tensile tester.

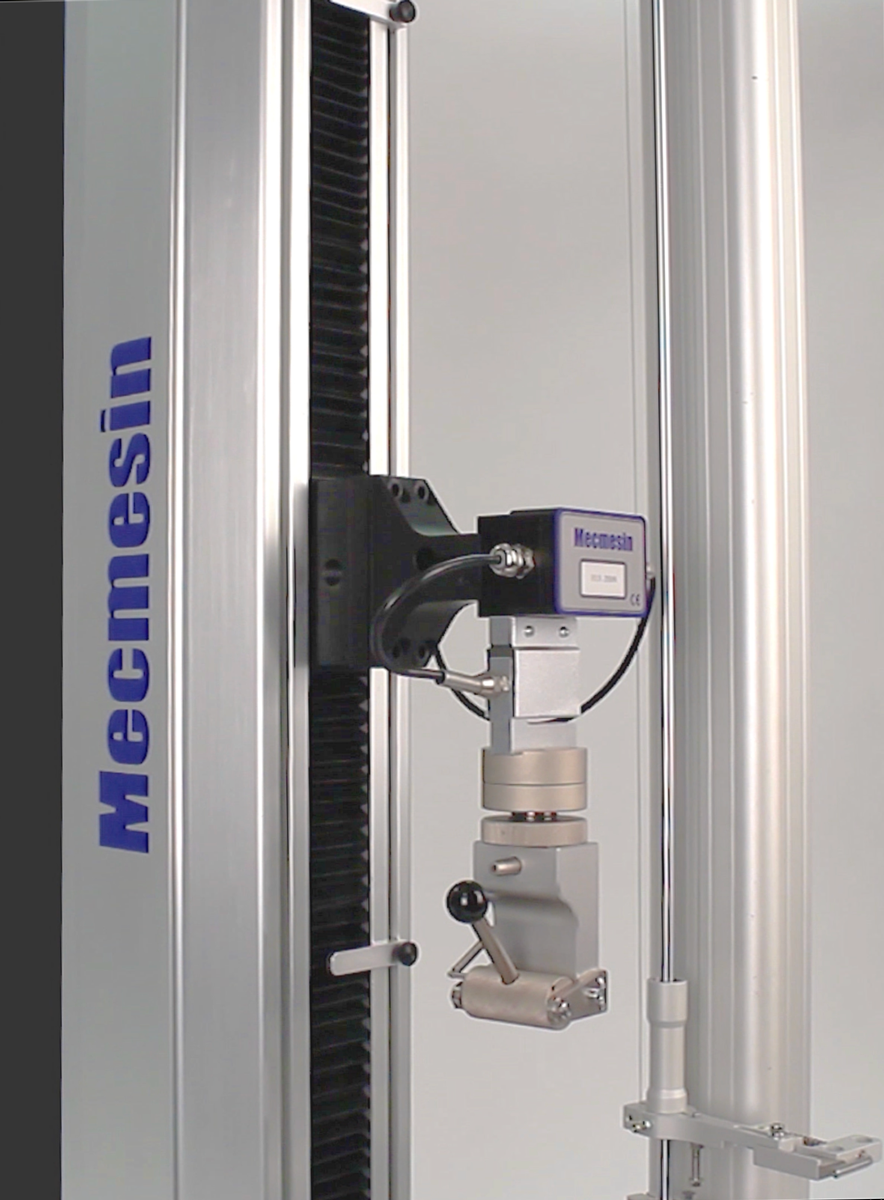
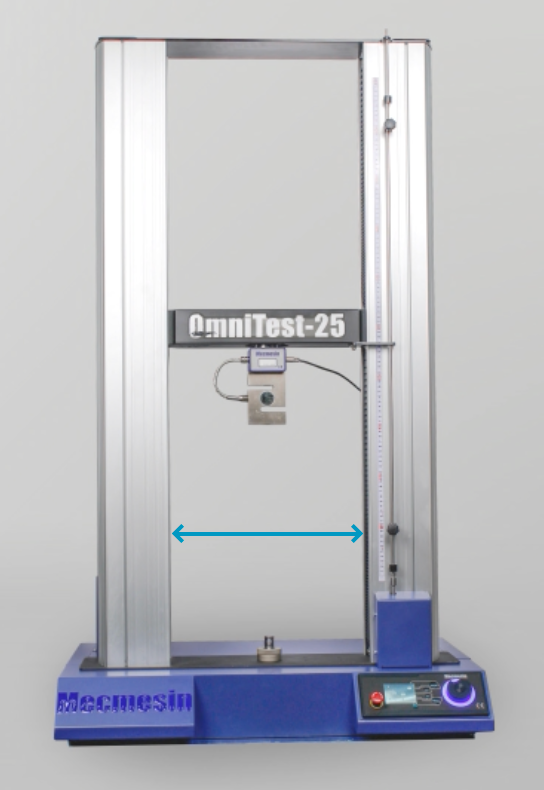 Calculating Workspace
Calculating Workspace
Tensile testers use a column structure to apply load, so it is important to check that your material or product can fit onto the test machine without hitting the column(s).
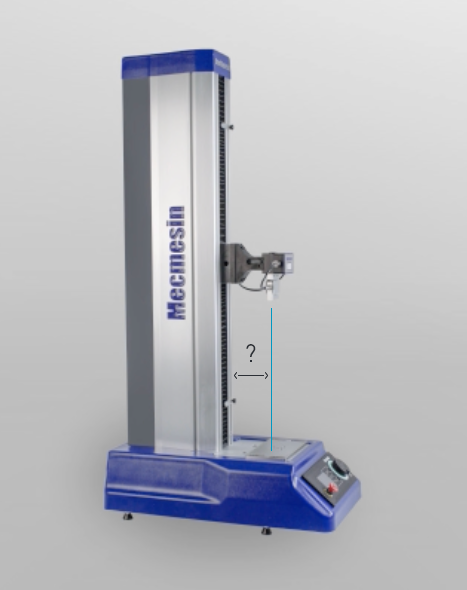
Single-column tensile testers have a workspace with a dimension called ‘throat-depth’, which is the distance between the loadcell and the column. Your specimen should be no greater than 2 x ‘throat depth’ otherwise it will not fit on the tester.
If your specimen size is too large you may need to consider a tensile tester with a large workspace even if it is nominally rated to a much higher load capacity than you need.
Choose the suitable travel stroke and workspace
- Identify the maximum travel distance required when the material or product is being stretched. Ensure that the tensile tester can accommodate your maximum stretch distance (known as “crosshead travel”).
- Check that the material or product you are testing can fit comfortably onto the workspace area of the tensile tester (known as ‘throat depth’).
- If ‘crosshead travel’ or ‘throat depth’ is insufficient you may need to consider a larger tensile tester even if it is nominally rated to a much higher load capacity than you need.



Having defined your test requirements and selected the load range you need, it is now time to consider the dimensional aspects of your testing.
Calculating Travel Distance
If you are performing tensile test you will need to identify the maximum travel distance required when the material or product is being stretched. Start with defining your initial specimen length and estimate the elongation that you expect to see. This will allow you to calculate the ‘crosshead travel’ that you require. Do not forget to include in your calculations the height of the grips you will use to hold the material/product, as these take up room on the tensile tester.


Tensile testers use a column structure to apply load, so it is important to check that your material or product can fit onto the test machine without hitting the column(s).
Single-column tensile testers have a workspace with a dimension called ‘throat-depth’, which is the distance between the loadcell and the column. Your specimen should be no greater than 2 x ‘throat depth’ otherwise it will not fit on the tester.
If your specimen size is too large you may need to consider a tensile tester with a large workspace even if it is nominally rated to a much higher load capacity than you need.
Testing speed
Answer
Consider the testing speed
- Determine the testing speed needed for your materials or products
- Choose a tensile tester that can operate at the required speed



The fourth step in choosing the right tensile tester is to consider the testing speed required for your testing application.
Testing Speed
Testing speed refers to the rate at which the tensile tester applies force to the specimen during testing. It is usually expressed in mm/min, in/min or load rate kN/second. Testing speed can vary depending on the type of materials or products being tested and the specific testing requirements. For example, testing a stiff metal beam may require load to be applied at a much slower test speed than when testing a very elastic piece of fabric.
Some tensile testers offer a selection of pre-set fixed speeds. Others offer infinitely variable testing speeds, which can be set by the user.
Make sure that you choose a tensile tester with a speed range to meet your testing requirements. The general rule is “the stiffer your material to be tested, the slower your tensile tester will need to move”.
Consider the testing speed
- Determine the testing speed needed for your materials or products
- Choose a tensile tester that can operate at the required speed



The fourth step in choosing the right tensile tester is to consider the testing speed required for your testing application.
Testing SpeedTesting speed refers to the rate at which the tensile tester applies force to the specimen during testing. It is usually expressed in mm/min, in/min or load rate kN/second. Testing speed can vary depending on the type of materials or products being tested and the specific testing requirements. For example, testing a stiff metal beam may require load to be applied at a much slower test speed than when testing a very elastic piece of fabric.
Some tensile testers offer a selection of pre-set fixed speeds. Others offer infinitely variable testing speeds, which can be set by the user.
Make sure that you choose a tensile tester with a speed range to meet your testing requirements. The general rule is “the stiffer your material to be tested, the slower your tensile tester will need to move”.
Environment
Answer
Consider the testing environment and conditions
- Determine the environmental conditions where the tensile tester will be located
- Decide which operators will use the tensile tester and their familiarity with using measuring equipment
- Choose a tensile tester that suits both the environmental conditions and ease-of-use criteria for your organisation
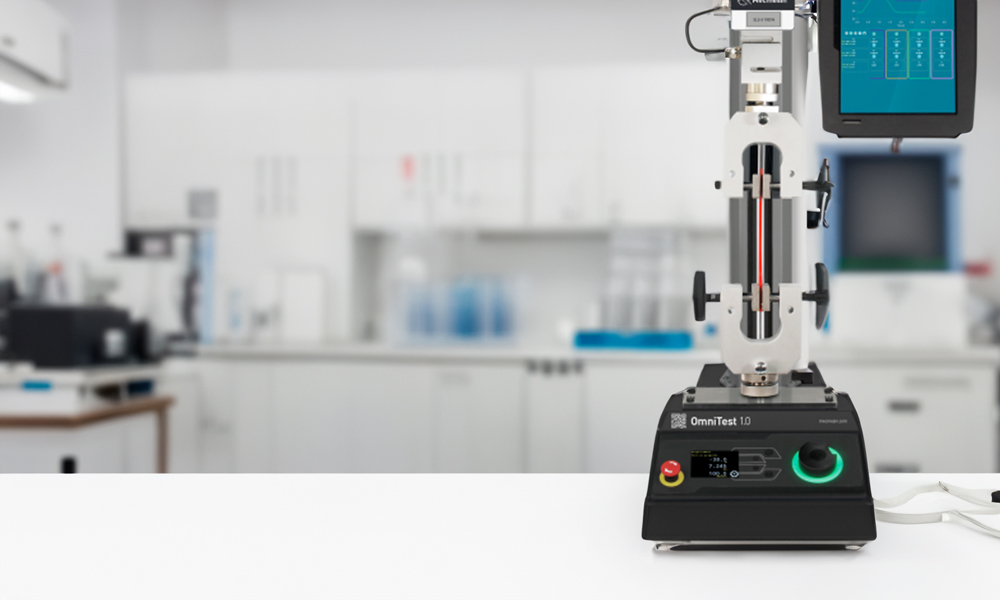
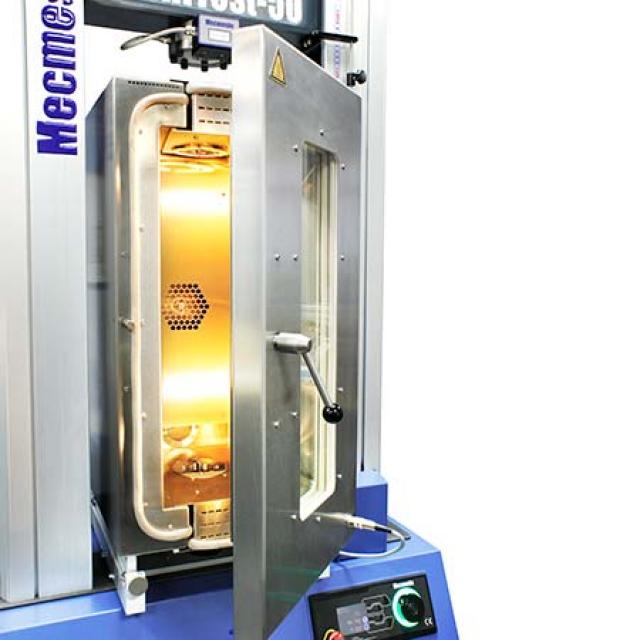



The fifth step in choosing the right tensile tester is to consider the testing environment and conditions in which the testing will be performed.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and corrosion can impact the performance and accuracy of a tensile tester. For example, if you will be testing materials in a humid or hot environment, it may be necessary to choose a tensile tester that is specifically designed to operate at elevated temperatures in high-humidity conditions.
Testing Conditions
In addition to environmental factors, it is important to consider where the tensile tester is planned to be situated. If the tester is placed in an area where other machinery is causing mechanical or electrical interference, it may adversely affect the measurements. This is particularly true when vibration can affect low-force tests.
It is also important to consider who will be performing testing on the tensile tester. If operators are trained metrologists they will be familiar with good working practices for measurement. However tensile testing is often performed by people who have other primary responsibilities. In this situation it is often beneficial to explore whether a tensile tester has a ‘simple’ operator mode that can assist users to quickly and easily perform tests.
By choosing a tensile tester that is designed to operate in your specific testing environment and conditions, you can ensure that you obtain accurate and reliable testing results that meet your specific needs.
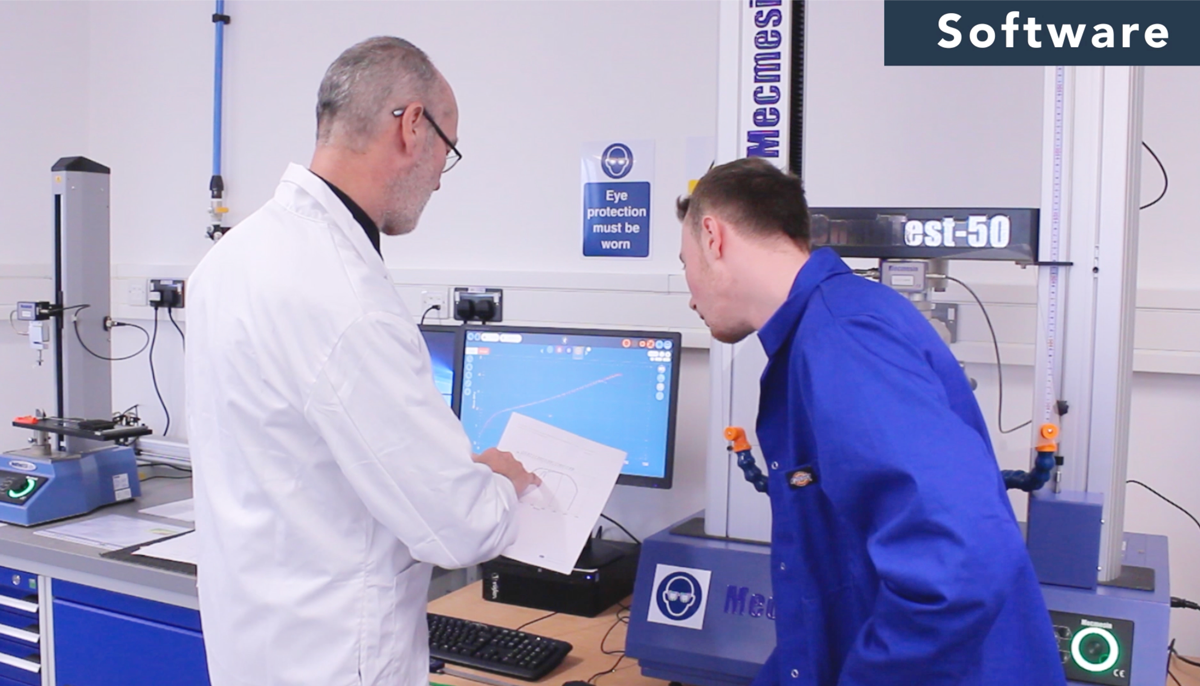

Consider the testing environment and conditions
- Determine the environmental conditions where the tensile tester will be located
- Decide which operators will use the tensile tester and their familiarity with using measuring equipment
- Choose a tensile tester that suits both the environmental conditions and ease-of-use criteria for your organisation



The fifth step in choosing the right tensile tester is to consider the testing environment and conditions in which the testing will be performed.
Environmental FactorsEnvironmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and corrosion can impact the performance and accuracy of a tensile tester. For example, if you will be testing materials in a humid or hot environment, it may be necessary to choose a tensile tester that is specifically designed to operate at elevated temperatures in high-humidity conditions.
Testing ConditionsIn addition to environmental factors, it is important to consider where the tensile tester is planned to be situated. If the tester is placed in an area where other machinery is causing mechanical or electrical interference, it may adversely affect the measurements. This is particularly true when vibration can affect low-force tests.
It is also important to consider who will be performing testing on the tensile tester. If operators are trained metrologists they will be familiar with good working practices for measurement. However tensile testing is often performed by people who have other primary responsibilities. In this situation it is often beneficial to explore whether a tensile tester has a ‘simple’ operator mode that can assist users to quickly and easily perform tests.
By choosing a tensile tester that is designed to operate in your specific testing environment and conditions, you can ensure that you obtain accurate and reliable testing results that meet your specific needs.

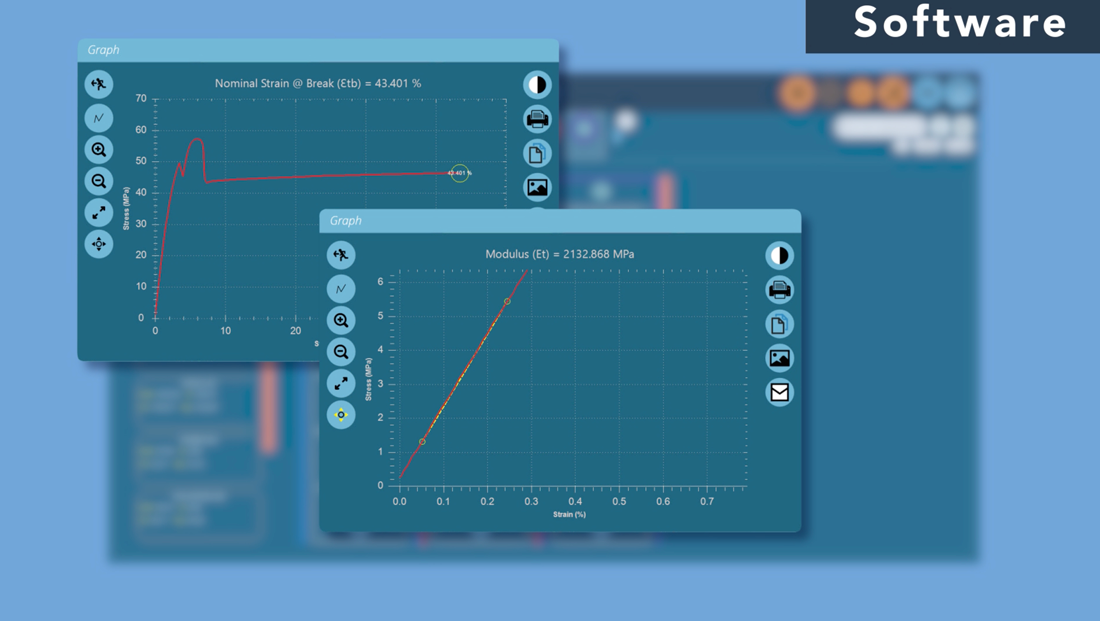
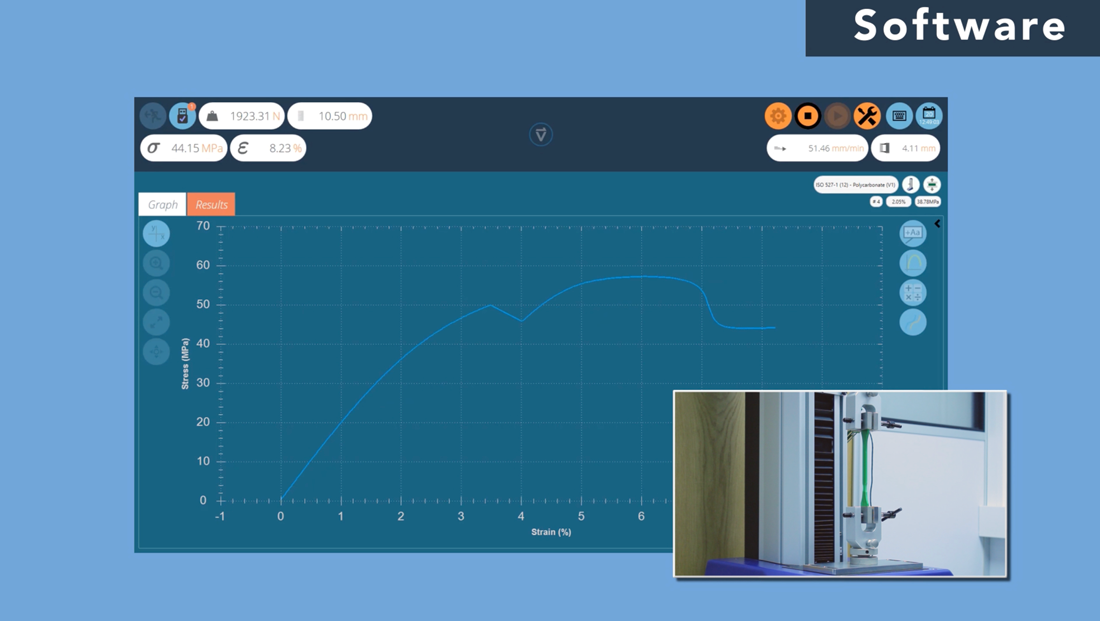
Software
Answer
Look at software and machine-control capabilities
- Identify any necessary software or data acquisition capabilities related to your current tests
- Consider whether you are likely to perform different tests in the future. Identify whether these tests require additional software capabilities
- Choose a tensile tester that provides the necessary software and data acquisition features to meet both your current and anticipated future requirements
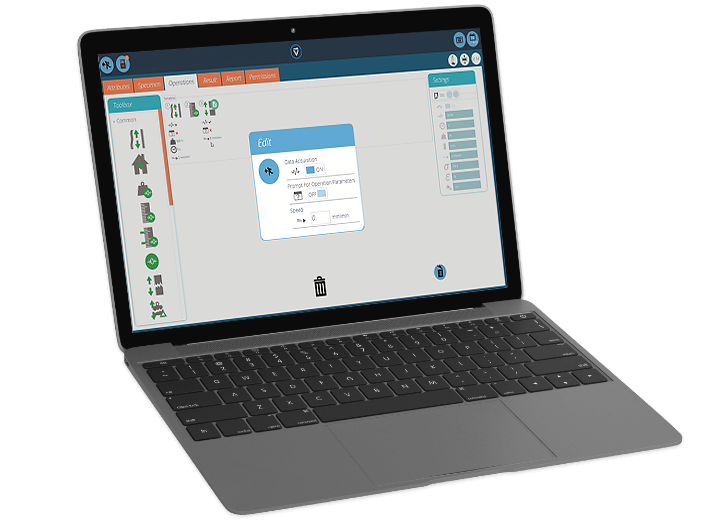
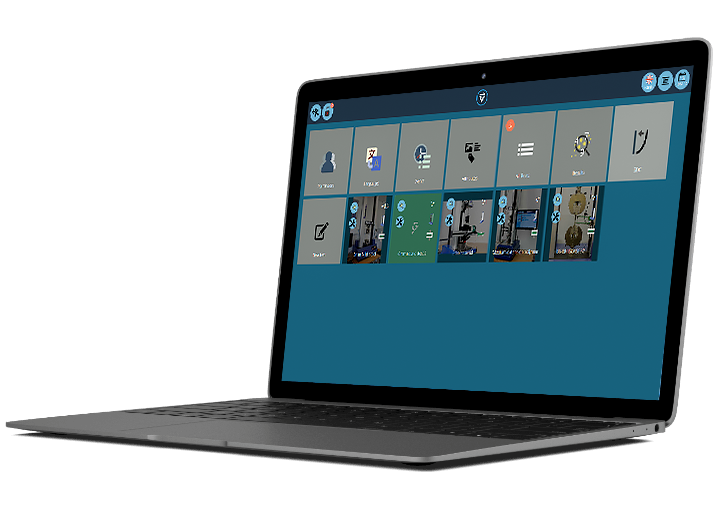
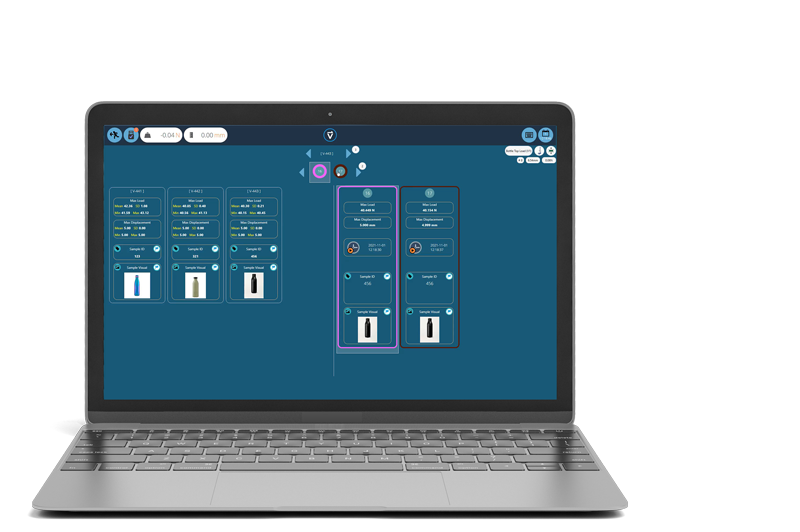
The ultimate and often decisive step in choosing the right tensile tester is to consider the software used to operate and control the tensile tester. The right software can help streamline testing processes, improve data analysis, reporting and increase overall efficiency and productivity.
Features of Tensile Tester Software
Tensile tester software can offer a variety of features, including:
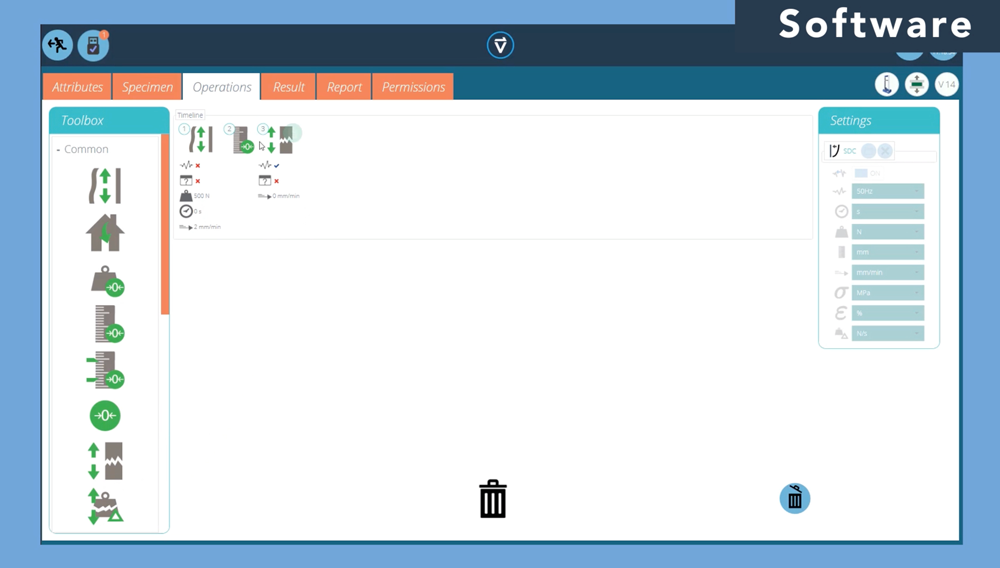
- User-friendly interface for straightforward operation and control of the tensile tester
- Real-time data acquisition, graphing and display of test results
- Customizable test methods to meet specific testing requirements
- Data analysis tools for performing statistical analysis and reporting
- Exporting data to other software programs, such as Excel or MATLAB
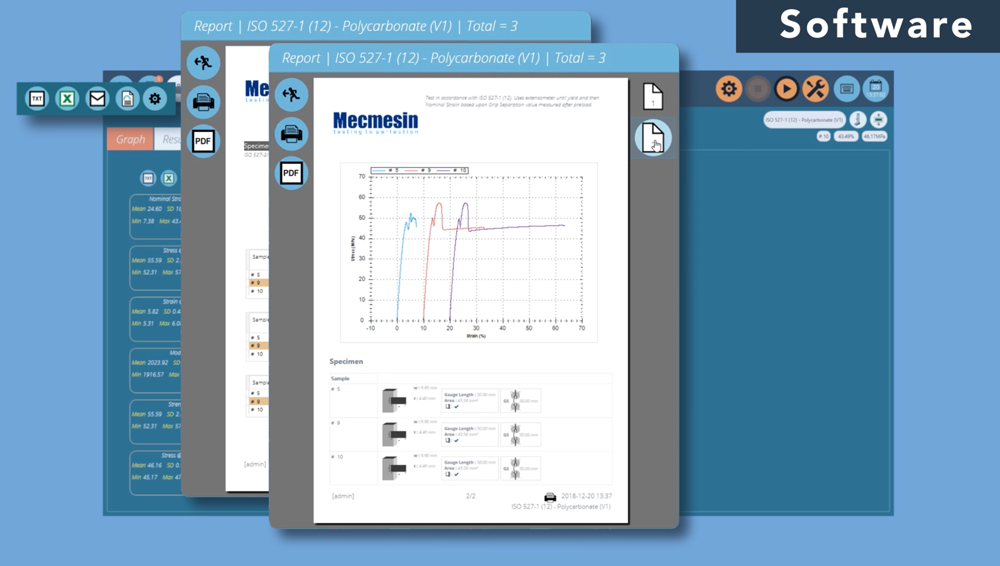
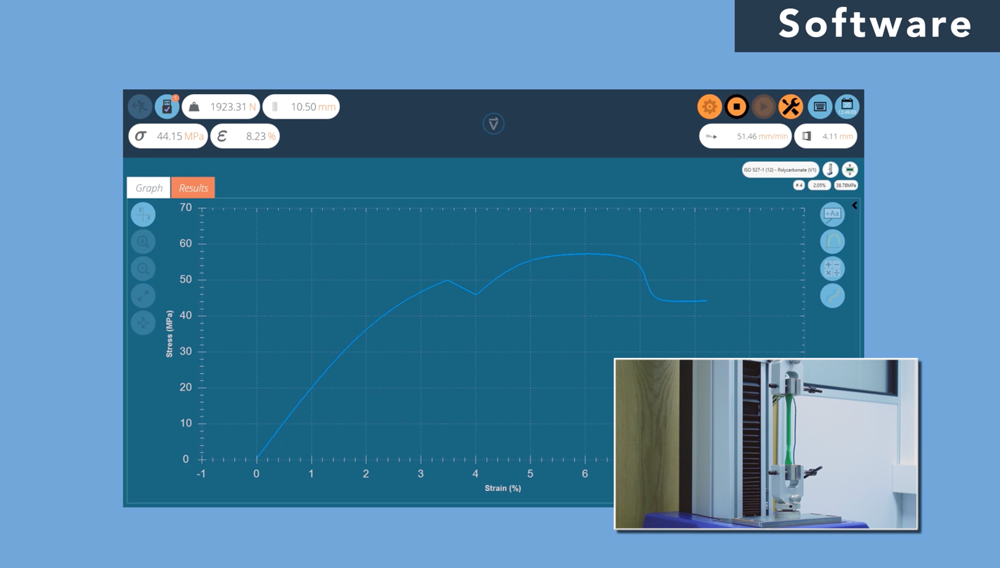
 Choosing the Right Tensile Tester Software for Your Needs
Choosing the Right Tensile Tester Software for Your Needs
When choosing a tensile tester you should look for software that is user-friendly and offers the features you need to meet your specific testing requirements.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that the tensile tester software is compatible with other software programs you may be using, such as data analysis or reporting tools.
By choosing the right tensile tester software, you can improve testing efficiency, accuracy, and data analysis, leading to better overall testing results and productivity.
Look at software and machine-control capabilities
- Identify any necessary software or data acquisition capabilities related to your current tests
- Consider whether you are likely to perform different tests in the future. Identify whether these tests require additional software capabilities
- Choose a tensile tester that provides the necessary software and data acquisition features to meet both your current and anticipated future requirements



The ultimate and often decisive step in choosing the right tensile tester is to consider the software used to operate and control the tensile tester. The right software can help streamline testing processes, improve data analysis, reporting and increase overall efficiency and productivity.
Features of Tensile Tester SoftwareTensile tester software can offer a variety of features, including:
- User-friendly interface for straightforward operation and control of the tensile tester
- Real-time data acquisition, graphing and display of test results
- Customizable test methods to meet specific testing requirements
- Data analysis tools for performing statistical analysis and reporting
- Exporting data to other software programs, such as Excel or MATLAB



When choosing a tensile tester you should look for software that is user-friendly and offers the features you need to meet your specific testing requirements.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that the tensile tester software is compatible with other software programs you may be using, such as data analysis or reporting tools.
By choosing the right tensile tester software, you can improve testing efficiency, accuracy, and data analysis, leading to better overall testing results and productivity.
Support
Answer
Consider after-sales support
- Consider your need for technical support for installation, training and ongoing software updates
- Consider who will provide the necessary periodic calibration and maintenance of the tensile tester
- Choose a supplier who will guarantee you prompt warranty and repair coverage in the event of any problems
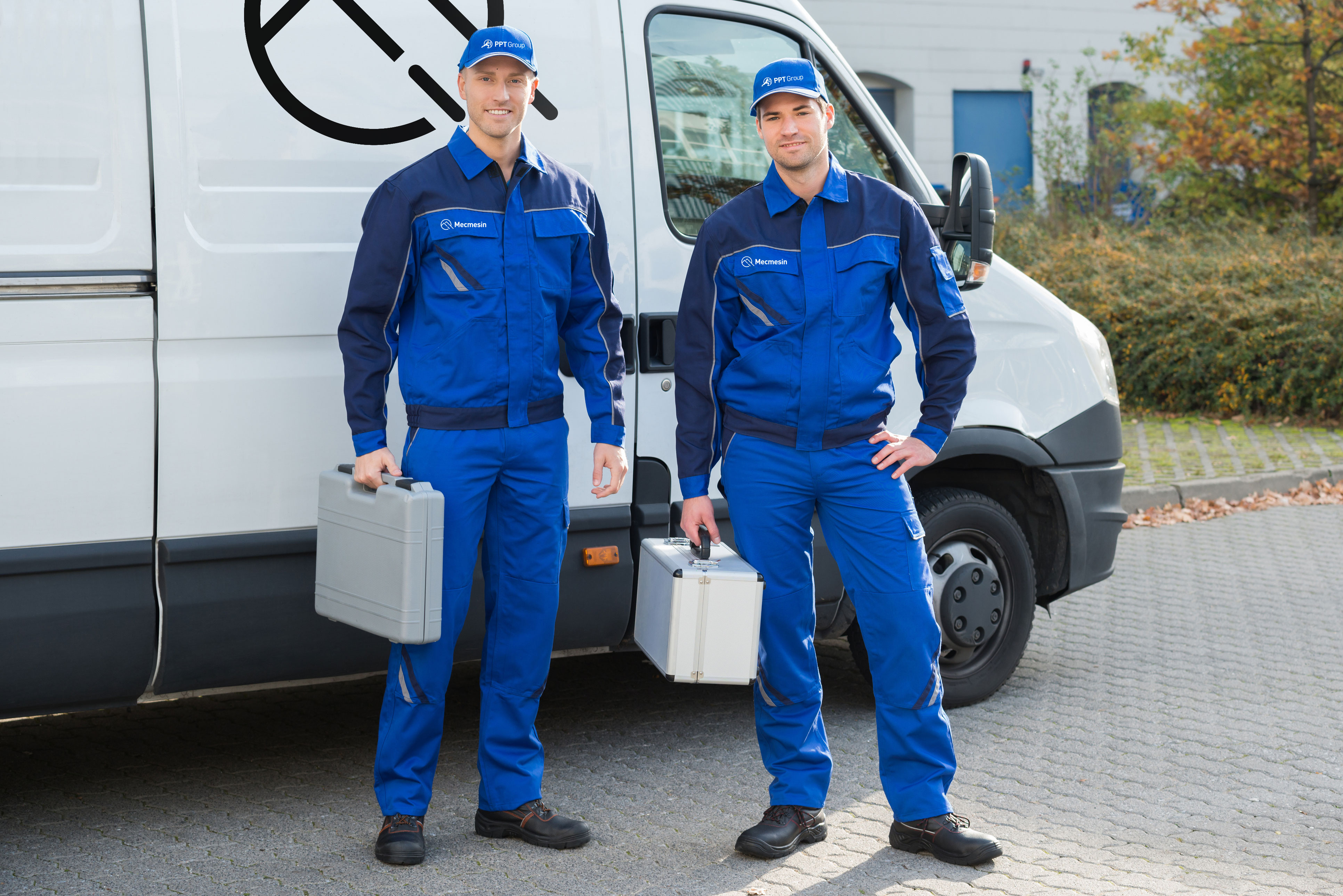


The last step in choosing the right tensile tester is to consider the after-sales support and service offered by the manufacturer or supplier. A reliable and responsive after-sales service can ensure that your tensile tester remains operational and provides accurate and reliable testing results for years to come.
After-Sales Support and Service Options
When considering after-sales support and service options, there are several factors to consider:
- Technical support: Does the manufacturer or supplier offer technical support to assist with any issues or questions that may arise during the operation of the tensile tester?
- Maintenance and calibration: Do the manufacturer or supplier offer maintenance and calibration services to ensure that the tensile tester is reading correctly and continues to operate accurately and reliably over time?
- Warranty and repair: What warranty options are available for the tensile tester, and what repair services are offered in the event of a malfunction or breakdown?
Choosing a Tensile Tester Supplier with Reliable After-Sales Support and Service
When choosing a tensile tester supplier, it is important to consider the after-sales support and service options they offer. Look for a supplier that offers comprehensive technical support, maintenance and calibration services, and a reliable warranty and repair service.
Choosing a supplier with reliable after-sales support and service can give you peace of mind knowing that any issues with your tensile tester will be quickly and efficiently resolved, allowing you to continue to obtain accurate and reliable testing results for years to come.

Consider after-sales support
- Consider your need for technical support for installation, training and ongoing software updates
- Consider who will provide the necessary periodic calibration and maintenance of the tensile tester
- Choose a supplier who will guarantee you prompt warranty and repair coverage in the event of any problems


The last step in choosing the right tensile tester is to consider the after-sales support and service offered by the manufacturer or supplier. A reliable and responsive after-sales service can ensure that your tensile tester remains operational and provides accurate and reliable testing results for years to come.
After-Sales Support and Service OptionsWhen considering after-sales support and service options, there are several factors to consider:
- Technical support: Does the manufacturer or supplier offer technical support to assist with any issues or questions that may arise during the operation of the tensile tester?
- Maintenance and calibration: Do the manufacturer or supplier offer maintenance and calibration services to ensure that the tensile tester is reading correctly and continues to operate accurately and reliably over time?
- Warranty and repair: What warranty options are available for the tensile tester, and what repair services are offered in the event of a malfunction or breakdown?
When choosing a tensile tester supplier, it is important to consider the after-sales support and service options they offer. Look for a supplier that offers comprehensive technical support, maintenance and calibration services, and a reliable warranty and repair service.
Choosing a supplier with reliable after-sales support and service can give you peace of mind knowing that any issues with your tensile tester will be quickly and efficiently resolved, allowing you to continue to obtain accurate and reliable testing results for years to come.

Budget
Answer
Set your budget
- Determine your budget for a tensile tester
- Choose a tester within your budget that provides the essential features and capabilities of your testing requirements. If your budget allows, select a tensile tester which will ‘future-proof’ your anticipated testing needs.
Armed with your complete technical requirements you are now in a position to start gathering quotations from suppliers of tensile testers.
This process will give you a good understanding of the different options open to you and will help you to establish a realistic budget for the acquisition of a testing system that will meet your needs for a number of years going forward.
Set your budget
- Determine your budget for a tensile tester
- Choose a tester within your budget that provides the essential features and capabilities of your testing requirements. If your budget allows, select a tensile tester which will ‘future-proof’ your anticipated testing needs.
Armed with your complete technical requirements you are now in a position to start gathering quotations from suppliers of tensile testers.
This process will give you a good understanding of the different options open to you and will help you to establish a realistic budget for the acquisition of a testing system that will meet your needs for a number of years going forward.



Want to test drive a tensile tester?
Talk to us about your tensile testing requirements and we can arrange a solution demo with tensile testing of your samples.
Outsourced tensile testing services can get expensive fast. PPT Group tensile testers make in-house testing easy, accurate and can save your business money.
Our solutions are easy to use, reliable and affordable with our expertise and support on-tap.
![1661-PDV14098-4-web.jpg Cosmetics brush pull-out [PDV14098]](/sites/default/files/styles/hero_766w/public/2023-10/1661-PDV14098-4-web.jpg.webp?itok=YBWbmt22)





















